INTRA-ARTICULAR THERAPY OF ARTHRITIS IN VARIOUS JOINTS:
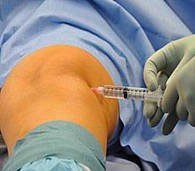
hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid acts as a lubricant for all joints. Hyaluronic acid is involved in the cross-linking of sugar protein chains in the cartilage and thus forms the basic lattice of the cartilage structure. Without hyaluronic acid, there is no firm and therefore no stable cartilage possible.
This fluid can reduce the friction resistance in the joint to a minimum and give stability in the event of movement.
Damaged and thus soft cartilage which can be reduced, can be stabilized again by a targeted hyaluronic acid delivery and the resilience can be increased.
